#8. Duomo

Duomo Brunelleschi Santa Maria del Fiore
 Duomo Location: Florence, Italy Architect: Filippo Brunelleschi Year: 1436
Duomo Location: Florence, Italy Architect: Filippo Brunelleschi Year: 1436
Pretty much the dome by which all other domes must be judged, Brunellschi’s Duomo caps the Florence Cathedral. Its construction was a radical decision, marking a break with the Gothic style and rejecting the notion that a flying buttress was required to support a massive dome. We will spare you the engineering details and state simply that this dome is an achievement of epic proportions.
The Basilica di Santa Maria del Fiore
 (English: Basilica of Saint Mary of the Flower) is the main church of Florence, Italy. Il Duomo di Firenze, as it is ordinarily called, was begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to the design of Arnolfo di Cambio and completed structurally in 1436 with the dome engineered by Filippo Brunelleschi. The exterior of the basilica is faced with polychrome marble panels in various shades of green and pink bordered by white and has an elaborate 19th-century Gothic Revival façade by Emilio De Fabris.
(English: Basilica of Saint Mary of the Flower) is the main church of Florence, Italy. Il Duomo di Firenze, as it is ordinarily called, was begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to the design of Arnolfo di Cambio and completed structurally in 1436 with the dome engineered by Filippo Brunelleschi. The exterior of the basilica is faced with polychrome marble panels in various shades of green and pink bordered by white and has an elaborate 19th-century Gothic Revival façade by Emilio De Fabris.
The cathedral complex, located in Piazza del Duomo, includes the Baptistery and Giotto’s Campanile. The three buildings are part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site covering the historic centre of Florence and are a major attraction to tourists visiting the region of Tuscany. The basilica is one of Italy’s largest churches, and until development of new structural materials in the modern era, the dome was the largest in the world. It remains the largest brick dome ever constructed.
The cathedral is the mother church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Florence, whose archbishop is currently Giuseppe Betori.
History
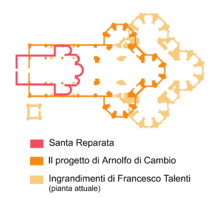
Santa Maria del Fiore was built on the site of an earlier cathedral dedicated to Saint Reparata. According to Bartlett, the cojonied by Arnolfo di Cambio and approved by city council in 1294. Arnolfo di Cambio was also architect of the church of Santa Croce and the Palazzo Vecchio. He designed three wide naves ending under the octagonal dome, with the middle nave covering the area of Santa Reparata. The first stone was laid on September 9, 1296 by Cardinal Valeriana, the first papal legate ever sent to Florence. The building of this vast project was to last 140 years, the collective efforts of several generations; Arnolfo’s plan for the eastern end, although maintained in concept, was greatly expanded in size.
 The Duomo, as if completed, in a fresco by Andrea di Bonaiuto, painted in the 1390s, before the commencement of the dome
The Duomo, as if completed, in a fresco by Andrea di Bonaiuto, painted in the 1390s, before the commencement of the dome
After Arnolfo died in 1302, work on the cathedral slowed for the following thirty years. When the relics of Saint Zenobius were discovered in 1330 in Santa Reparata, the project obtained new impetus. In 1331, the Arte della Lana, the guild of wool merchants, took over exclusive patronage for the construction of the cathedral and in 1334 appointed Giotto to oversee the work. Assisted by Andrea Pisano, Giotto continued di Cambio’s design. His major accomplishment was the building of the campanile. When Giotto died in 1337, Andrea Pisano continued the building until work was again halted due to the Black Death in 1348.
In 1349 work resumed on the cathedral under a series of architects, commencing with Francesco Talenti, who finished the campanile and enlarged the overall project to include the apse and the side chapels. In 1359 Talenti was succeeded by Giovanni di Lapo Ghini(1360–1369) who divided the center nave in four square bays. Other architects were Alberto Arnoldi, Giovanni d’Ambrogio, Neri di Fioravante and Andrea Orcagna. By 1375 the old church Santa Reparata was pulled down. The nave was finished by 1380, and by 1418 only the dome remained incomplete.
 Procession outside the cathedral during the 18th century
Procession outside the cathedral during the 18th century
On 18 August 1418, the Arte della Lana announced a structural design competition for erecting Neri’s dome. The two main competitors were two master goldsmiths, Lorenzo Ghiberti and Filippo Brunelleschi, who was supported by Cosimo de Medici. Ghiberti had been winner of a competition for a pair of bronze doors for the Baptistery in 1401 and lifelong competition between the two remained acute. Brunelleschi won and received the commission.
Ghiberti, appointed coadjutator, was drawing a salary equal to Brunelleschi’s and, though neither was awarded the announced prize of 200 florins, would potentially earn equal credit, while spending most of his time on other projects. When Brunelleschi became ill, or feigned illness, the project was briefly in the hands of Ghiberti. But Ghiberti soon had to admit that the whole project was beyond him. In 1423 Brunelleschi was back in charge and took over sole responsibility.
Work started on the dome in 1420 and was completed in 1436. The cathedral was consecrated by Pope Eugene IV on March 25, 1436 (the first day of the year according to the Florentine calendar). It was the first ‘octagonal’ dome in history to be built without a temporary wooden supporting frame: the Roman Pantheon, a circular dome, was built in 117–128 AD with support structures. It was one of the most impressive projects of the Renaissance. During the consecration service in 1436, Guillaume Dufay‘s similarly unique motet Nuper rosarum flores was performed. The structure of this motet was strongly influenced by the structure of the dome.
 The Duomo and Baptistery of St. John from Piazza del Duomo
The Duomo and Baptistery of St. John from Piazza del Duomo
The decoration of the exterior of the cathedral, begun in the 14th century, was not completed until 1887, when the polychrome marble façade was completed to the design of Emilio De Fabris. The floor of the church was relaid in marble tiles in the 16th century.
The exterior walls are faced in alternate vertical and horizontal bands of polychrome marble from Carrara (white), Prato (green), Siena (red), Lavenza and a few other places. These marble bands had to repeat the already existing bands on the walls of the earlier adjacent baptistery the Battistero di San Giovanni and Giotto’s Bell Tower. There are two lateral doors, the Doors of the Canonici (south side) and the Door of the Mandorla (north side) with sculptures by Nanni di Banco, Donatello, and Jacopo della Quercia. The six lateral windows, notable for their delicate tracery and ornaments, are separated by pilasters. Only the four windows closest to the transept admit light; the other two are merely ornamental. The clerestory windows are round, a common feature in Italian Gothic.
During its long history, this cathedral has been the seat of the Council of Florence (1439), heard the preachings of Girolamo Savonarola and witnessed the murder of Giuliano di Piero de’ Medici on Sunday, 26 April 1478 (with Lorenzo Il Magnifico barely escaping death) in the Pazzi conspiracy.
Exterior – Plan and Structure
The cathedral of Florence is built as a basilica, having a wide central nave of four square bays, with an aisle on either side. The chancel and transepts are of identical polygonal plan, separated by two smaller polygonal chapels. The whole plan forms a Latin cross. The nave and aisles are separated by wide pointed Gothic arches resting on composite piers.
The dimensions of the building are enormous: length 153 metres (502 ft), width 38 metres (124 ft), width at the crossing 90 metres (295 ft). The height of the arches in the aisles is 23 metres (75 ft). The height of the dome is 114.5 m.
Dome
By the beginning of the 15th century, after a hundred years of construction, the structure was still missing its dome. The basic features of the dome had been designed by Arnolfo di Cambio in 1296. His brick model, 4.6 metres (15 ft) high 9.2 metres (30 ft) long, was standing in a side aisle of the unfinished building, and had long ago become sacrosanct. It called for an octagonal dome higher and wider than any that had ever been built, with no external buttresses to keep it from spreading and falling under its own weight.
The commitment to reject traditional Gothic buttresses had been made when Neri di Fioravante’s model was chosen over a competing one by Giovanni di Lapo Ghini. That architectural choice, in 1367, was one of the first events of the Italian Renaissance, marking a break with the Medieval Gothic style and a return to the classic Mediterranean dome. Italian architects regarded Gothic flying buttresses as ugly makeshifts and since the use of buttresses was forbidden in Florence, in addition to being a style favored by central Italy’s traditional enemies to the north. Neri’s model depicted a massive inner dome, open at the top to admit light, like Rome’s Pantheon, but enclosed in a thinner outer shell, partly supported by the inner dome, to keep out the weather. It was to stand on an unbuttressed octagonal drum. Neri’s dome would need an internal defense against spreading (hoop stress), but none had yet been designed.
 Dome seen from the Giotto’s Campanile
Dome seen from the Giotto’s Campanile
The building of such a masonry dome posed many technical problems. Brunelleschi looked to the great dome of the Pantheon in Rome for solutions. The dome of the Pantheon is a single shell of concrete, the formula for which had long since been forgotten. A wooden form had held the Pantheon dome aloft while its concrete set, but for the height and breadth of the dome designed by Neri, starting 52 metres (171 ft) above the floor and spanning 44 metres (144 ft), there was not enough timber in Tuscany to build the scaffolding and forms. Brunelleschi chose to follow such design and employed a double shell, made of sandstone and marble. Brunelleschi would have to build the dome out of bricks, due to its light weight compared to stone and easier to form, and with nothing under it during construction. To illustrate his proposed structural plan, he constructed a wooden and brick model with the help of Donatello and Nanni di Banco which is still displayed in the Museo dell’Opera del Duomo. The model served as a guide for the craftsmen, but was intentionally incomplete, so as to ensure Brunelleschi’s control over the construction.
Brunelleschi’s solutions were ingenious. The spreading problem was solved by a set of four internal horizontal stone and iron chains, serving as barrel hoops, embedded within the inner dome: one each at the top and bottom, with the remaining two evenly spaced between them. A fifth chain, made of wood, was placed between the first and second of the stone chains. Since the dome was octagonal rather than round, a simple chain, squeezing the dome like a barrel hoop, would have put all its pressure on the eight corners of the dome. The chains needed to be rigid octagons, stiff enough to hold their shape, so as not to deform the dome as they held it together.
Each of Brunelleschi’s stone chains was built like an octagonal railroad track with parallel rails and cross ties, all made of sandstone beams 43 centimetres (17 in) in diameter and no more than 2.3 metres (7.5 ft) long. The rails were connected end-to-end with lead-glazed iron splices. The cross ties and rails were notched together and then covered with the bricks and mortar of the inner dome. The cross ties of the bottom chain can be seen protruding from the drum at the base of the dome. The others are hidden. Each stone chain was supposed to be reinforced with a standard iron chain made of interlocking links, but a magnetic survey conducted in the 1970s failed to detect any evidence of iron chains, which if they exist are deeply embedded in the thick masonry walls. He was also able to accomplish this by setting vertical “ribs” on the corners of the octagon curving towards the center point. The Ribs, 13 feet (4 meters) deep, are supported by 16 concealed ribs radiating from center. The ribs had slits to take beams that supported platforms, thus allowing the work to progress upward without the need for scaffolding.
A circular masonry dome, such as that of Hagia Sophia in Istanbul can be built without supports, called centering, because each course of bricks is a horizontal arch that resists compression. In Florence, the octagonal inner dome was thick enough for an imaginary circle to be embedded in it at each level, a feature that would hold the dome up eventually, but could not hold the bricks in place while the mortar was still wet. Brunelleschi used a herringbone brick pattern to transfer the weight of the freshly laid bricks to the nearest vertical ribs of the non-circular dome.
The outer dome was not thick enough to contain embedded horizontal circles, being only 60 centimetres (2 ft) thick at the base and 30 centimetres (1 ft) thick at the top. To create such circles, Brunelleschi thickened the outer dome at the inside of its corners at nine different elevations, creating nine masonry rings, which can be observed today from the space between the two domes. To counteract hoop stress, the outer dome relies entirely on its attachment to the inner dome at its base; it has no embedded chains.
A modern understanding of physical laws and the mathematical tools for calculating stresses was centuries into the future. Brunelleschi, like all cathedral builders, had to rely on intuition and whatever he could learn from the large scale models he built. To lift 37,000 tons of material, including over 4 million bricks, he invented hoisting machines and lewissons for hoisting large stones. These specially designed machines and his structural innovations were Brunelleschi’s chief contribution to architecture. Although he was executing an aesthetic plan made half a century earlier, it is his name, rather than Neri’s, that is commonly associated with the dome.
Brunelleschi’s ability to crown the dome with a lantern was questioned and he had to undergo another competition. He was declared the winner over his competitors Lorenzo Ghiberti and Antonio Ciaccheri. His design (now on display in the Museum Opera del Duomo) was for an octagonal lantern with eight radiating buttresses and eight high arched windows. Construction of the lantern was begun a few months before his death in 1446. Then, for 15 years, little progress was possible, due to alterations by several architects. The lantern was finally completed by Brunelleschi’s friend Michelozzo in 1461. The conical roof was crowned with a gilt copper ball and cross, containing holy relics, by Verrocchio in 1469. This brings the total height of the dome and lantern to 114.5 metres (375 ft). This copper ball was struck by lightning on 17 July 1600 and fell down. It was replaced by an even larger one two years later.
The commission for this bronze ball [atop the lantern] went to the sculptor Andrea del Verrocchio, in whose workshop there was at this time a young apprentice named Leonardo da Vinci. Fascinated by Filippo’s [Brunelleschi’s] machines, which Verrocchio used to hoist the ball, Leonardo made a series of sketches of them and, as a result, is often given credit for their invention.
Leonardo might have also participated in the design of the bronze ball, as stated in the G manuscript of Paris “Remember the way we soldered the ball of Santa Maria del Fiore.”
The decorations of the drum gallery by Baccio d’Agnolo were never finished after being disapproved by no one less than Michelangelo.
A huge statue of Brunelleschi now sits outside the Palazzo dei Canonici in the Piazza del Duomo, looking thoughtfully up towards his greatest achievement, the dome that would forever dominate the panorama of Florence. It is still the largest masonry dome in the world.
The building of the cathedral had started in 1296 with the design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was completed in 1469 with the placing of Verrochio’s copper ball atop the lantern. But the façade was still unfinished and would remain so until the 19th century.
http://www.complex.com/art-design/2011/02/the-top-50-architectural-achievements-of-the-modern-world/duomo