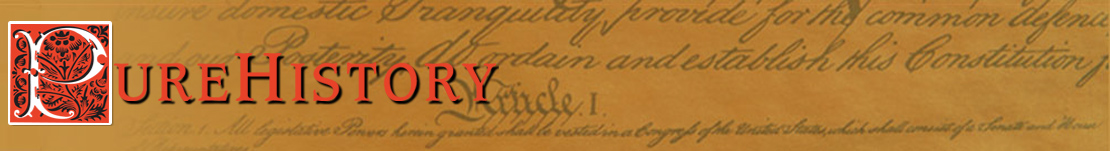Bermuda

The Birth of a Trust: Bermuda’s History Through Music
The Birth of a Trust: Bermuda’s History through Music (1997: Dread & Baha Productions) is a documentary about the history of entertainment in Bermuda seen through the eyes of many of the country’s most notable musicians. The film documents the evolution of local music scene from the big band era of the 1940’s and 1950’s, through the popular “Battle of the Groups” at the Rosebank in the late 60s and 70s, up to the dancehall clashes of today. It features local legends like Hubert Smith, Ghandi Burgess, Lance Hayward and Michael Curtis Clarke and highlights the accomplishments of present day artists like Ras Giorgis and now retired soundsystem “Playboy International”. The film also discusses how the music of the time reflected the social changes that were taking place at any particular point in our history; from WWII, to the volatile 60’s and 70’s with the assesination of the Governor and the riots, and the 1981 general strike.
Bermuda /bɜrˈmjuːdə/, in full The Islands of Bermuda, also referred to as the Bermudas or the Somers Isles, is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean, located off the east coast of the United States. Its nearest landmassis Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, about 1,030 kilometres (640 mi) to the west-northwest. It is about 1,239 kilometres (770 mi) south of Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia, and 1,770 kilometres (1,100 mi) northeast of Miami. Its capital city is Hamilton.
Bermuda was discovered in 1505 by Spanish sea captain Juan de Bermúdez, after whom the islands are named. He claimed the apparently uninhabited islands for the Spanish Empire. Although he paid two visits to the archipelago, Bermúdez never landed on the islands because he did not want to risk crossing over the dangerous reef surrounding them. Subsequent Spanish or other visitors are believed to have released the feral pigs that were abundant on the island when European settlement began. In 1609, the Virginia Company, which had established Virginia and Jamestown on the American continent two years earlier, established a settlement, founded in the aftermath of a hurricane, when the crew of the sinking Sea Venture steered it on the reef so they could get ashore.
It was first administered as an extension of Virginia by the Company until 1614, before its successor, the Somers Isles Company, took over until 1684. At that time, the company’s charter was revoked and the Crown took over administration. The islands became a British colony following the 1707 unification of the parliaments of Scotland and England, which created the Kingdom of Great Britain. After Newfoundland became part of Canada in 1949, Bermuda became the oldest (and, since the return of Hong Kong to China in 1997, the most populous) remaining British Overseas Territory. Its first capital, St. George’s, was established in 1612. It is the oldest continuously inhabited English town in the New World.
Bermuda’s economy is based on offshore insurance and reinsurance, and tourism; the two largest economic sectors. Bermuda had one of the world’s highest GDP per capita for most of the 20th century and several years beyond. Recently, its economic status has been affected by the global recession. It has a subtropicalclimate. Bermuda is the northernmost point of the so-called Bermuda Triangle, a region of sea in which, according to legend, a number of aircraft and surface vessels have disappeared under supposedly unexplained or mysterious circumstances. The island is in the hurricane belt and prone to severe weather.
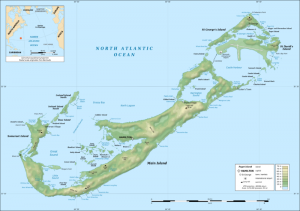
Although usually referred to in the singular, the territory consists of 181 islands, with a total area of 53.3 square kilometres (20.6 square miles). The largest island is Main Island, sometimes called Bermuda. Compiling a list of the islands is often complicated, as many have more than one name (as does the entire archipelago, which has also been known historically as La Garza, Virgineola, and the Isle of Devils. Somers Isles is often rendered “Somers Islands”, or mistaken for “Summer Isles”). Despite its small land mass, place names are repeated; there are, for example, two islands namedLong Island, three bays named Long Bay (on Somerset, Main, and Cooper’s islands), two Horseshoe Bays (one in Warwick, on the Main Island, the other at Morgan’s Point, formerly Tucker’s Island), there are two roads through cuttings called Khyber Pass (one in Warwick, the other in St. George’s Parish), and St George’s Town is located on St George’s Island within St George’s Parish (each known as St George’s). There is a Hamilton Parish in addition to the City of Hamilton (which is in Pembroke Parish).
-
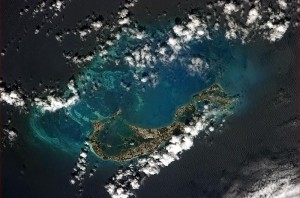
Bermuda pictured from the International Space Station
Climate of Bermuda
 Residential scene in Bermuda
Residential scene in Bermuda
Bermuda has a humid subtropical climate on the border of tropical climate. It is warmed by the nearby Gulf Stream, due to the westerlies, which carry warm, humid air eastwards over Bermuda, helping to keep winter temperatures above freezing. The climate is humid and, as a result, the summertime heat index can be high, even though mid-August temperatures rarely exceed 30 °C (86 °F). Winters are mild and windy, with average daytime temperatures in January and February around 20 °C (68 °F), although cold fronts bring Arctic air masses that can result in rapid temperature drops. Atlantic winter storms, often associated with these cold fronts, can produce powerful, gusting winds and heavy rain. Factoring in the wind chill, the felt air temperature in winter can fall below freezing, 0 °C (32 °F), even though the actual temperature rarely drops below 10 °C(50 °F). The lowest temperature recorded between 1949 and 1999 was 6.7 °C (44 °F), in February 1950.
Bermuda is within the hurricane belt. Located along the Gulf Stream, it is often directly in the path of hurricanes recurving in the westerlies, although they usually begin to weaken as they approach the island. The island’s small size means that direct landfalls of hurricanes are rare. The last hurricane to cause significant damage to Bermuda was category 3 Hurricane Fabian on 5 September 2003.
The only source of fresh water in Bermuda is rainfall, which is collected on roofs and catchments (or drawn from underground lenses) and stored in tanks. Each dwelling usually has at least one of these tanks forming part of its foundation.
The average annual temperature of the sea is 73.1 °F (22.8 °C), from 65.4 °F (18.6 °C) in February to 82.8 °F (28.2 °C) in August.