The American Civil War
American Civil War – The Complete History
The American Civil War, widely known as simply the Civil War in the United States as well as other sectional names, was fought from 1861 to 1865. Seven Southern slave states individually declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America, known as the “Confederacy” or the “South”. They grew to include eleven states, and although they claimed thirteen states and additional western territories, the Confederacy was never recognized by a foreign country. The states that did not declare secession were known as the “Union” or the “North”. The war had its origin in the fractious issue of slavery, especially the extension of slavery into the western territories.[N 1] After four years of bloody combat that left over 600,000 Union and Confederate soldiers dead and destroyed much of the South’s infrastructure, the Confederacy collapsed, slavery was abolished, and the difficult Reconstruction process of restoring national unity and guaranteeing civil rights to the freed slaves began.
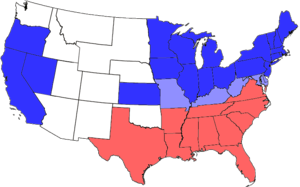
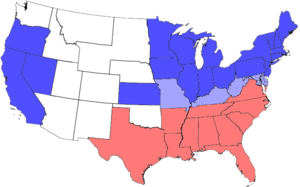 United States Divided 1861-1865
United States Divided 1861-1865
The American Civil War (1861–1865) was a civil war in the United States of America. Eleven Southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America, also known as “the Confederacy.” Led by Jefferson Davis, the Confederacy fought for its independence from the United States. The U.S. federal government was supported by twenty mostly-Northern free states in which slavery already had been abolished, and by five slave states that became known as the border states. These twenty-five states, referred to as the Union, had a much larger base of population and industry than the South. After four years of bloody, devastating warfare (mostly within the Southern states), the Confederacy surrendered and slavery was outlawed everywhere in the nation. The restoration of the Union, and the Reconstruction Era that followed, dealt with issues that remained unresolved for generations.
In the presidential election of 1860, the Republican Party, led by Abraham Lincoln, had campaigned against the expansion of slavery beyond the states in which it already existed. The Republicans were strong advocates of nationalism and in their 1860 platform explicitly denounced threats of disunion as avowals of treason. After a Republican victory, but before the new administration took office on March 4, 1861, seven cotton states declared their secession and joined together to form the Confederate States of America. Both the outgoing administration of President James Buchanan and the incoming administration rejected the legality of secession, considering it rebellion. The other eight slave states rejected calls for secession at this point. No country in the world recognized the Confederacy.
Hostilities began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked a U.S. military installation at Fort Sumter in South Carolina. Lincoln responded by calling for a volunteer army from each state to recapture federal property. This led to declarations of secession by four more slave states. Both sides raised armies as the Union seized control of the border states early in the war and established a naval blockade that virtually ended cotton sales on which the South depended for its wealth, and blocked most imports. Land warfare in the East was inconclusive in 1861–62, as the Confederacy beat back Union efforts to capture its capital, Richmond, Virginia. In September 1862, Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation made ending slavery in the South a war goal, and dissuaded the British from intervening.
Confederate commander Robert E. Lee won battles in Virginia, but in 1863 his northward advance was turned back with heavy casualties after the Battle of Gettysburg. To the west, the Union gained control of the Mississippi River after their capture of Vicksburg, Mississippi, thereby splitting the Confederacy in two. The Union was able to capitalize on its long-term advantages in men and materiel by 1864 when Ulysses S. Grant fought battles of attrition against Lee, while Union general William Tecumseh Sherman captured Atlanta and marched to the sea. Confederate resistance ended after Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Court House on April 9, 1865.
The American Civil War was one of the earliest true industrial wars. Railroads, the telegraph, steamships, and mass-produced weapons were employed extensively. The practices of total war, developed by Sherman in Georgia, and of trench warfare around Petersburg foreshadowed World War I in Europe. It remains the deadliest war in American history, resulting in the deaths of 620,000 soldiers and an undetermined number of civilian casualties. Ten percent of all Northern males 20–45 years of age died, as did 30 percent of all Southern white males aged 18–40. Victory for the North meant the end of the Confederacy and of slavery in the United States, and strengthened the role of the federal government. The social, political, economic and racial issues of the war decisively shaped the reconstruction era that lasted to 1877.
Filmography Andersonville (1996) The Birth of a Nation (1915) The Blue and the Gray (1982 TV series) The Civil War (1990) Civil War Minutes: Confederate (2007) Civil War Minutes: Union (2001) Cold Mountain (2003) The Colt (2005) Dog Jack (2010) Gettysburg (1993) Glory (1989) Gods and Generals (2003) Gone with the Wind (1939) The Good The Bad and The Ugly (1967) The Hunley (1999) North and South (TV miniseries) Trilogy (1985, 1986, 1994) The Red Badge of Courage (1951) Ride with the Devil (1999) Shenandoah (1965) Sommersby (1993).
The American Civil War (1861–1865), often referred to as The Civil War in the United States, was a civil war fought over the secession of the Confederate States. 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America (“the Confederacy”); the other 25 states supported the federal government (“the Union“). After four years of warfare, mostly within the Southern states, the Confederacy surrendered and slavery was outlawed everywhere in the nation. Issues that led to war were partially resolved in the Reconstruction Era that followed, though others remained unresolved.
In the presidential election of 1860, the Republican Party, led by Abraham Lincoln, had campaigned against expanding slavery beyond the states in which it already existed. The Republicans strongly advocated nationalism, and in their 1860 platform they denounced threats of disunion as avowals of treason. After a Republican victory, but before the new administration took office on March 4, 1861, seven cotton states declared their secession and joined to form the Confederate States of America. Both the outgoing administration of President James Buchanan and the incoming administration rejected the legality of secession, considering it rebellion. The other eight slave states rejected calls for secession at this point. No foreign governments recognized the Confederacy.
Hostilities began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked a U.S. military installation at Fort Sumter in South Carolina. Lincoln responded by calling for a volunteer army from each state to recapture federal property, which led to declarations of secession by four more slave states. Both sides raised armies as the Union seized control of the border states early in the war and established a naval blockade. Land warfare in the East was inconclusive in 1861–62, as the Confederacy beat back Union efforts to capture its capital, Richmond, Virginia, notably during the Peninsular Campaign. In September 1862, the Confederate campaign in Maryland ended in defeat at the Battle of Antietam, which dissuaded the British from intervening. Days after that battle, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which made ending slavery a war goal.
Life of Robert E. Lee
Watch a short biography video of Robert E. Lee, the leader of the Confederate forces during the American Civil War. Learn more about Robert E. Lee: http://bit.ly/19855ZI. Watch more videos about Robert E. Lee: http://bit.ly/1eWLtfZ. Learn more about American Military Leaders: http://bit.ly/128esal. Learn more about West Point Alumni: http://bit.ly/16dJBIR. Robert E. Lee came to military prominence during the U.S. Civil War, commanding Virginia’s armed forces and becoming general-in-chief of the Confederate forces.
 Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War.
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War.
The son of Revolutionary War officer Henry “Light Horse Harry” Lee III and a top graduate of the United States Military Academy, Robert E. Lee distinguished himself as an exceptional officer and combat engineer in the United States Army for 32 years. During this time, he served throughout the United States, distinguished himself during the Mexican-American War, served as Superintendent of the United States Military Academy, and married Mary Custis.
When Virginia declared its secession from the Union in April 1861, Lee chose to follow his home state, despite his personal desire for the Union to stay intact and despite the fact that President Abraham Lincoln had offered Lee command of the Union Army. During the Civil War, Lee originally served as a senior military adviser to President Jefferson Davis. He soon emerged as a shrewd tactician and battlefield commander, winning numerous battles against larger Union armies. His abilities as a tactician have been praised by many military historians. His strategic vision was more doubtful, and both of his invasions of the North ended in defeat. Union General Ulysses S. Grant‘s campaigns bore down on Lee in 1864 and 1865, and despite inflicting heavy casualties, Lee was unable to force back Grant. Lee would ultimately surrender to Grant at Appomattox Court Houseon April 9, 1865. By this time, Lee had been promoted to the commanding officer of all Confederate forces; the remaining armies soon capitulated after Lee’s surrender. Lee rejected the starting of a guerrilla campaign against the North and called for reconciliation between the North and South.
General Ulysses S. Grant: Mr. Lincoln’s Butcher
After the war, as President of what is now Washington and Lee University, Lee supported President Andrew Johnson‘s program of Reconstruction and intersectional friendship, while opposing the Radical Republican proposals to give freed slaves the vote and take the vote away from ex-Confederates. He urged them to rethink their position between the North and the South, and the reintegration of former Confederates into the nation’s political life. Lee became the great Southern hero of the War, a postwar icon of the “Lost Cause of the Confederacy” to some. But his popularity grew even in the North, especially after his death in 1870. He remains an iconic figure of American military leadership.
In 1863, Confederate general Robert E. Lee’s northward advance ended in defeat at the Battle of Gettysburg. To the west, the Union gained control of the Mississippi River after the Battle of Shiloh and Siege of Vicksburg, splitting the Confederacy in two and destroying much of their western army. Due to his western successes, Ulysses S. Grant was given command of all Union armies in 1864, and organized the armies of William Tecumseh Sherman, Philip Sheridan and others to attack the Confederacy from all directions, increasing the North’s advantage in manpower. Grant restructured the union army, and put other generals in command of divisions of the army that were to support his push into Virginia. He fought several battles of attrition against Lee through the Overland Campaign to seize Richmond, though in the face of fierce resistance he altered his plans and led the Siege of Petersburg which nearly finished off the rest of Lee’s army. Meanwhile, Sherman captured Atlanta and marched to the sea, destroying Confederate infrastructure along the way. When the Confederate attempt to defend Petersburg failed, the Confederate army retreated but was pursued and defeated, which resulted in Lee’s surrender to Grant at Appomattox Court House on April 9, 1865.
The American Civil War was one of the earliest true industrial wars. Railroads, the telegraph, steamships, and mass-produced weapons were employed extensively. The practices of total war, developed by Sherman in Georgia, and of trench warfare around Petersburg foreshadowed World War I in Europe. It remains the deadliest war in American history, resulting in the deaths of an estimated 750,000 soldiers and an undetermined number of civilian casualties. Historian John Huddleston estimates the death toll at ten percent of all Northern males 20–45 years old, and 30 percent of all Southern white males aged 18–40. Victory for the North meant the end of the Confederacy and of slavery in the United States, and strengthened the role of the federal government. The social, political, economic and racial issues of the war decisively shaped the reconstruction era that lasted to 1877.