D-Day: Normandy Landings
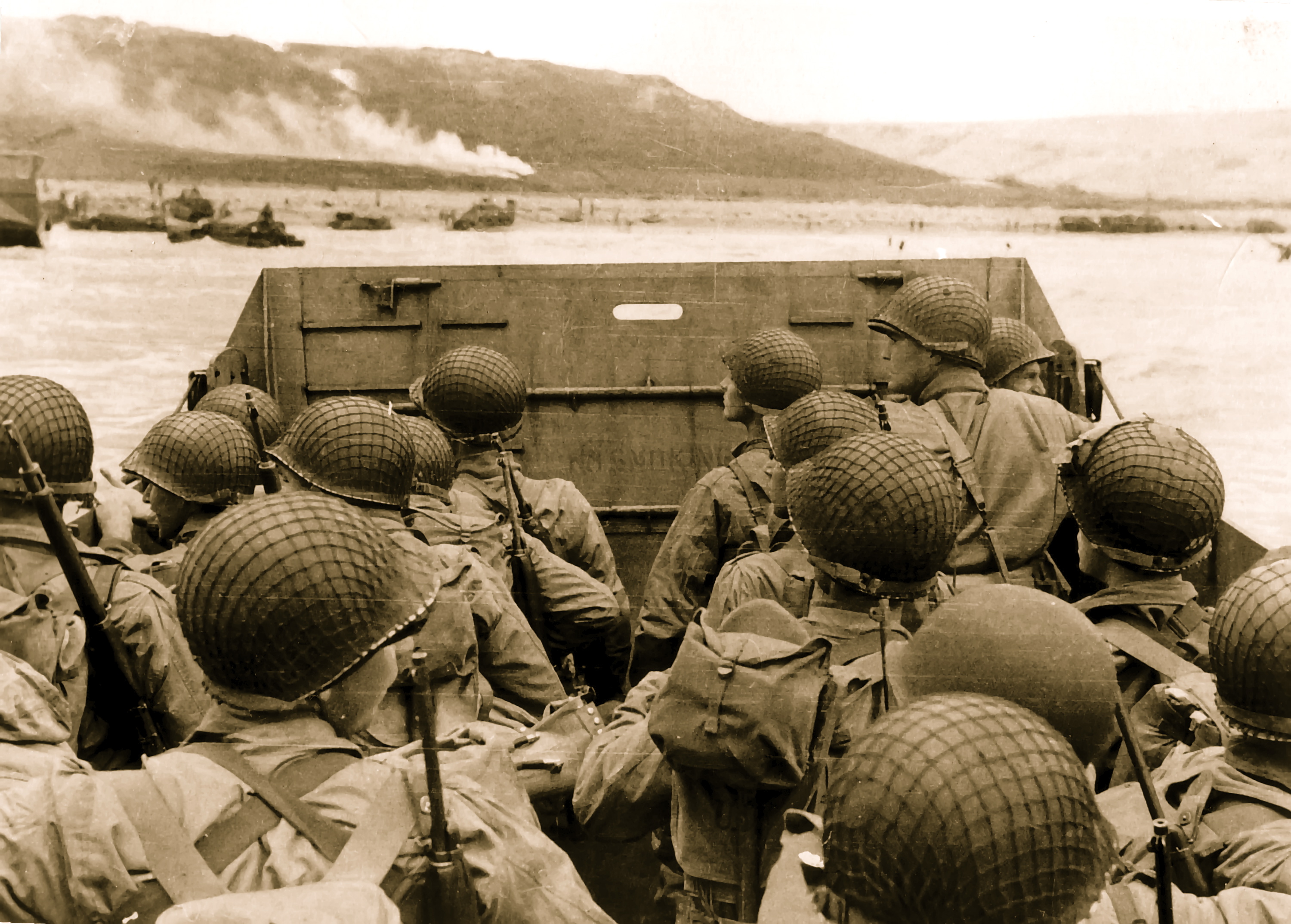

Uncut Chronicles: D-Day 1944. Archive footage of Invasion Forces & Defences
The 70th anniversary of the largest seaborne invasion in written history and one of the turning points of WWII — the Normandy landings — is being marked in style and with tears of joy as people remember veterans’ bravery and sacrifice. The Normandy landings were the landing operations on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during WWII. Archive footage consists of the following fragments: General Eisenhower and his aides look at wall map as they plan the invasion of Normandy France, Operation Overlord in 1944. Slave labors building the German “West Wall” defense system of fortifications along the coast of Europe. Various scenes of large gun emplacements. The hugh stockpile of tanks, trucks, artillery guns, bombs, aircraft, and other supplies amassed in England to support the Allied invasion of European Continent. The naval armada assembled to transport the troops, war equipment, and supplies across the English Channel. Unloading of landing barges from decks of ships. Troops practice loading operations. The armada of ships underway across the English Channel for the invasion of Normandy France. On June 6, 1944 planes loaded with paratroopers of the 101st and 82nd Airborne Divisions spearheaded the Normandy invasion by jumping behind the German lines and coastal defenses. Paratroopers jumping from C-47 aircraft. Landing craft underway to beachhead firing artillery guns. Rocket ship firing barrage of rockets. Allied troops landing on beachheads on D-Day. Soldiers using flame throwers and charges to destroy gun fortifications. Troops wade ashore from landing craft under cover of barrage balloons. RT LIVE http://rt.com/on-air.
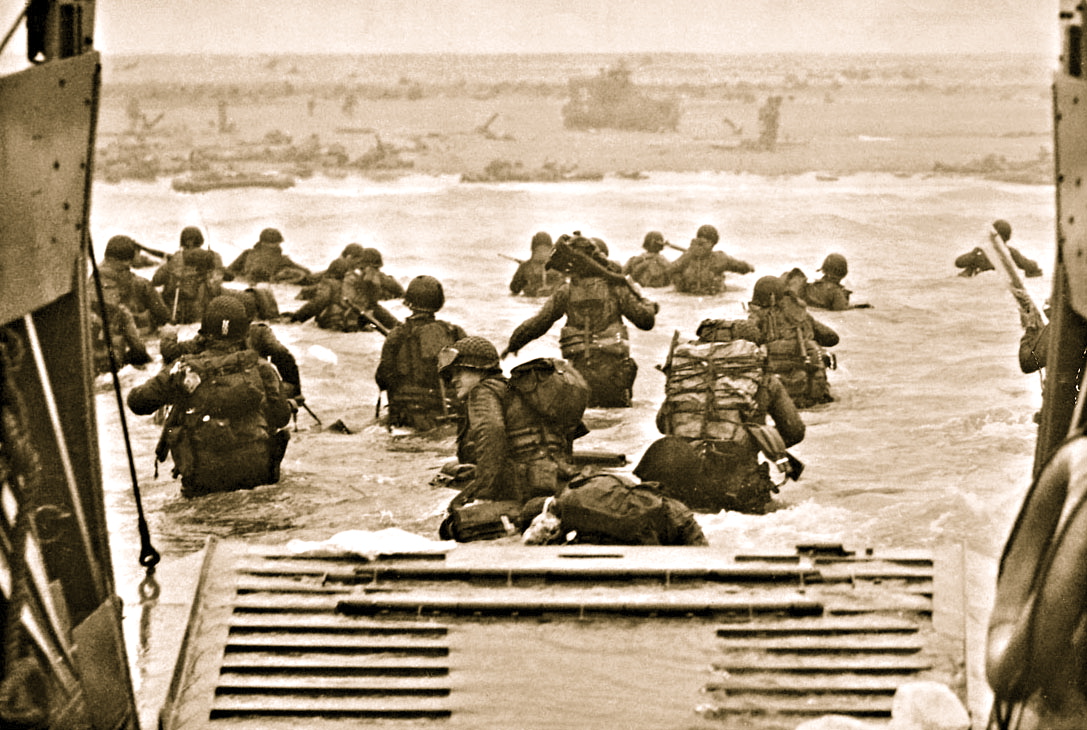
 US Army troops wade ashore on Omaha Beach on the morning of 6 June 1944
US Army troops wade ashore on Omaha Beach on the morning of 6 June 1944
The Normandy landings, codenamed Operation Neptune, were the landing operations on 6 June 1944 (termed D-Day) of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. The largest seaborne invasion in history, the operation began the invasion of German-occupied western Europe, led to the restoration of the French Republic, and contributed to an Allied victory in the war.
Planning for the operation began in 1943. In the months leading up to the invasion, the Allies conducted a substantial military deception, codenamed Operation Bodyguard, to mislead the Germans as to the date and location of the main Allied landings. The weather on D-Day was far from ideal, but postponing would have meant a delay of at least two weeks, as the invasion planners had requirements for the phase of the moon, the tides, and the time of day that meant only a few days in each month were deemed suitable. Hitler placed German Field Marshal Erwin Rommel in command of German forces and of developing fortifications along the Atlantic Wall in anticipation of an Allied invasion.
The amphibious landings were preceded by extensive aerial and naval bombardment and an airborne assault—the landing of 24,000 British, US, and Canadian airborne troops shortly after midnight. Allied infantry and armoured divisions began landing on the coast of France starting at 06:30. The target 50-mile (80 km) stretch of the Normandy coast was divided into five sectors: Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno and Sword Beach. Strong winds blew the landing craft east of their intended positions, particularly at Utah and Omaha. The men landed under heavy fire from gun emplacements overlooking the beaches, and the shore was mined and covered with obstacles such as wooden stakes, metal tripods, and barbed wire, making the work of the beach clearing teams difficult and dangerous. Casualties were heaviest at Omaha, with its high cliffs. At Gold, Juno, and Sword, several fortified towns were cleared in house-to-house fighting, and two major gun emplacements at Gold were disabled using specialised tanks.
 The Allies failed to achieve all of their goals on the first day. Carentan, St. Lô, and Bayeux remained in German hands, and Caen, a major objective, was not captured until 21 July. Only two of the beaches (Juno and Gold) were linked on the first day, and all five bridgeheads were not connected until 12 June. However, the operation gained a foothold that the Allies gradually expanded over the coming months. German casualties on D-Day were around 1,000 men. Allied casualties were at least 12,000, with 4,414 confirmed dead. Museums, memorials, and war cemeteries in the area host many visitors each year.
The Allies failed to achieve all of their goals on the first day. Carentan, St. Lô, and Bayeux remained in German hands, and Caen, a major objective, was not captured until 21 July. Only two of the beaches (Juno and Gold) were linked on the first day, and all five bridgeheads were not connected until 12 June. However, the operation gained a foothold that the Allies gradually expanded over the coming months. German casualties on D-Day were around 1,000 men. Allied casualties were at least 12,000, with 4,414 confirmed dead. Museums, memorials, and war cemeteries in the area host many visitors each year.